![Electrical hand tools list everyone should own]()
You need the right tools to work safely and efficiently with electricity. Every electrician relies on a core set of basic electrician tools to get the job done right. As of 2022, over 760,000 electricians in the United States use these tools every day, and the demand keeps growing. Whether you are starting out or have years of experience, building your electrical hand tools list helps you stay prepared. > Remember, choosing quality tools boosts your safety and the quality of your work.
Electrical hand tools list
A complete electrical hand tools list helps you work safely and efficiently. You need to know which tools to choose and how to use them. This section breaks down the most essential hand tools for every electrician. Each tool serves a specific purpose and meets strict safety standards. You can use this guide to build your own toolkit or check if you have the right equipment.
Pliers
Pliers are some of the most important hand tools for any electrician. You use them to grip, cut, bend, and twist wires. Industry associations recommend several types of pliers for electrical work. These include lineman’s pliers, needle-nose pliers, and channel lock pliers. Each type has unique features that make certain tasks easier and safer.
Lineman’s Pliers
Lineman’s pliers are a staple in every electrical hand tools list. You rely on them for gripping, twisting, and cutting wires. The wide, flat jaws help you hold wires firmly. The cutting edge slices through thick wires and cables. Many electricians use lineman’s pliers to splice wires or pull fish tape. High-quality lineman’s pliers have ergonomic handles and insulated grips. These features reduce hand fatigue and protect you from electric shock. Certified lineman’s pliers can withstand up to 1000 volts AC and 1500 volts DC, meeting strict safety standards. You should always check for certification from a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) to ensure compliance with the National Electrical Code.
Tip: Choose lineman’s pliers with precision cutting edges and a smooth, stable joint. This ensures durability and makes your work easier.
Needle-Nose Pliers
Needle-nose pliers are essential for working in tight spaces. You use them to reach wires inside junction boxes or electrical panels. The long, slender jaws let you bend, twist, and shape wires with accuracy. Many electricians use needle-nose pliers to loop wire ends or hold small components. Look for models with insulated handles and fine tips. This design gives you better control and keeps you safe during electrical work. Needle-nose pliers also help you retrieve dropped screws or wires from hard-to-reach places.
Channel Lock Pliers
Channel lock pliers, also called pump pliers, give you a strong grip on pipes, conduit, and large connectors. You can adjust the jaw width to fit different sizes. Electricians often use channel lock pliers to tighten or loosen nuts and bolts. The serrated jaws prevent slipping and provide a secure hold. Choose channel lock pliers with insulated handles for extra protection. A good pair will have a smooth joint and ergonomic design to reduce hand strain.
Wire Cutters
Wire cutters are a must-have on any electrical hand tools list. You use them to cut wires cleanly and safely. Different types of wire cutters suit different tasks. Diagonal cutters, also known as side cutters or dikes, work well for small wires and tight spaces. Heavy-duty cutters or ratcheting cable cutters handle thick wires and cables. Flush cutters make neat cuts on tiny wires, which is useful for electronics. Always choose wire cutters with insulated handles and sharp blades. This ensures clean cuts and protects you from electrical hazards. You should match the cutter type to the wire gauge for the best results.
Diagonal cutters: Best for small to medium gauge wires.
Cable cutters: Designed for thick cables.
Flush cutters: Ideal for precision work on small wires.
Wire Strippers
Wire strippers help you remove insulation from wires without damaging the metal inside. You need them for almost every electrical job. Most wire strippers have marked holes for different wire gauges. This feature lets you strip wires accurately and quickly. Always select the right size for the wire you are working with. Using the wrong size can nick or break the wire. Many electricians prefer wire strippers with adjustable blades and ergonomic handles. These features make the tool comfortable and efficient.
Safety Note: Always turn off the power before using wire strippers. Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from flying debris and electrical hazards.
You should never use wire strippers as a hammer or for tasks they are not designed for. Regularly check the blades for sharpness and keep the tool clean. Insulated wire strippers provide extra safety, but do not use them on live circuits unless they are rated for that purpose.
Cable Cutters
Cable cutters are essential when you need to cut large electrical cables cleanly and safely. You will find that cable cutters differ from wire cutters in both function and design. While wire cutters handle smaller wires, cable cutters are built for heavy-duty jobs. You use them to cut thick cables, such as those found in main service panels or industrial settings. Using the right tool from your electrical hand tools list prevents damage to both the tool and the cable.
Here is a quick comparison to help you choose the correct tool:
| Tool Type | Function | Recommended Use |
| Wire Cutters | Designed for cutting smaller wires and conductors; often multifunctional (stripping, crimping). | Suitable for smaller gauge wires; tasks requiring precision and clean cuts without damaging insulation or conductors. |
| Cable Cutters | Specialized for cutting larger conductors and cables; available in manual and ratcheting designs. | Recommended for larger gauge cables and heavy-duty applications; ratcheting cutters reduce fatigue and provide cleaner cuts on thick cables (e.g., 4/0 AWG). Power tools may be needed for very large cables. |
You should select cable cutters based on the size and type of cable you work with most often. Manual cable cutters work well for occasional use, but ratcheting models reduce hand fatigue and make cleaner cuts on thick cables. Always match the cutter to the cable gauge. Using the wrong tool can damage the blade or crush the cable, which leads to unsafe connections.
Tip: Keep your cable cutters sharp and clean. Dull blades require more force and can slip, increasing the risk of injury.
When you build your electrical hand tools list, include both wire cutters and cable cutters. This ensures you have the right tool for every job and helps you maintain safety and efficiency.
Utility Knife
A utility knife is a versatile tool you will use for many tasks in electrical work. You rely on it to strip cable sheathing, cut insulation, and open boxes. A sharp utility knife makes your work faster and more precise. However, improper use can lead to serious injuries.
Common injuries from utility knives include:
Hand lacerations and cuts
Puncture wounds
Amputations of fingers or parts of the hand
Stabbing wounds to hands, arms, or legs
These injuries often happen when the knife slips or when you use too much force. Drawing the knife toward your body, using a dull blade, or storing the knife with the blade extended increases the risk. Many accidents occur because workers do not wear cut-resistant gloves or fail to inspect the knife before use.
To stay safe, follow these best practices:
Always cut away from your body.
Replace dull blades promptly.
Use a self-retracting knife when possible.
Wear cut-resistant gloves.
Store the knife with the blade retracted or covered.
Inspect the knife before each use to ensure the blade is secure.
Note: OSHA reports that dull blades cause more injuries because they require extra force, which increases the chance of slips and serious cuts.
When you add a utility knife to your hand tools, choose one with a comfortable grip and a secure blade-locking mechanism. This small tool plays a big role in your electrical hand tools list, helping you work efficiently and safely.
Must have electrician tools
Every electrician needs a reliable set of must have electrician tools to work safely and efficiently. Leading trade organizations agree that certain tools belong in every toolkit. You should focus on safety, efficiency, and the ability to handle a wide range of electrical tasks. This section highlights the most important electrician tools you need for any job.
Insulated Screwdrivers
Insulated screwdrivers are among the most must have electrician tools. You use them to tighten or loosen screws in outlets, panels, and fixtures. These tools protect you from electric shock when working near live circuits. High-quality insulated screwdrivers meet strict safety standards, including IEC 60900 and ASTM F1505. Manufacturers test these tools to withstand up to 1000 V AC, giving you a strong safety margin. Always check for markings that show the voltage rating, manufacturer, and certification.
| Feature | Details |
| Voltage Rating | Up to 1000 V AC |
| Standards | IEC 60900, ASTM F1505, VDE |
| Markings | Manufacturer, tool type, double-triangle symbol, voltage rating, year, standard |
| Temperature Rating | Standard: -20°C; Category C: -40°C |
| Additional Safety | Use with voltage-rated gloves for best protection |
Tip: Always inspect your insulated screwdrivers before use. Look for cracks or damage in the insulation.
Flathead
Flathead screwdrivers have a straight, flat blade. You use them for screws with a single slot. These screws appear in outlets, switches, and older electrical panels. Flathead screwdrivers are must have electrician tools because many electrical devices still use slotted screws. Choose a model with a comfortable grip and a blade that fits the screw head snugly. This reduces the risk of slipping and damaging the screw or surrounding components.
Phillips
Phillips screwdrivers have a cross-shaped tip. You use them for screws with a plus-shaped slot. Most modern electrical devices use Phillips screws because they provide better grip and reduce the chance of stripping. A Phillips screwdriver is one of the must have electrician tools for installing outlets, switches, and light fixtures. Select an insulated model that matches the screw size for the best results.
Nut Drivers
Nut drivers are essential tools for every electrician. You use them to tighten or loosen hex-head nuts and bolts. These fasteners appear in panel boards, circuit breakers, and electrical enclosures. Nut drivers give you better control and alignment than pliers or adjustable wrenches. You can work quickly and avoid damaging delicate components. Many electricians prefer nut drivers for their precision and convenience, especially when working on electronics, appliances, or HVAC systems.
Nut drivers fit small hex nuts and bolts found in electrical hardware.
They help you avoid over-tightening, which can damage sensitive parts.
You can use nut drivers in tight spaces where other tools do not fit.
Note: Nut drivers are must have electrician tools for low-torque applications that require accuracy and a gentle touch.
Adjustable Wrench
An adjustable wrench is another must have electrician tool. You use it to grip and turn nuts and bolts of different sizes. The movable jaw lets you adjust the tool to fit various fasteners. This versatility means you do not need to carry multiple fixed-size wrenches. Electricians often use adjustable wrenches when working with conduit fittings, cable glands, or mounting hardware. The tool saves space in your toolkit and adapts to many situations.
Adjustable wrenches provide flexibility for different fastener sizes.
You can carry fewer tools and still handle most electrical tasks.
The tool works well in environments where you encounter a variety of bolt sizes.
Tip: Always make sure the jaws of your adjustable wrench fit snugly on the fastener. Loose jaws can slip and damage the bolt or cause injury.
When you build your set of must have electrician tools, focus on safety, efficiency, and quality. Choose tools with insulated handles, ergonomic designs, and clear markings. These features help you work faster and reduce the risk of accidents. Every electrician benefits from a well-chosen set of electrician tools that meet the demands of both residential and industrial work.
Crimping Tool
A crimping tool is one of the must have electrician tools you need for making secure wire connections. You use this tool to attach connectors to the ends of wires. This process creates a strong, reliable joint that will not loosen over time. Many electrical projects require crimped connections, especially when you work with terminals like ring, spade, or butt connectors.
When you choose a crimping tool for your electrician tools kit, look for these key features:
Wire Gauge Compatibility: Select a tool that matches the wire sizes you use most often, usually from 10 AWG to 22 AWG.
Terminal Type Compatibility: Make sure your tool works with the connector types you need, such as ring or spade terminals.
Application-Specific Needs: Pick a compact tool for tight spaces or a faster tool for high-volume jobs.
Quality Materials and Construction: Hardened steel dies and ergonomic handles improve durability and comfort.
Compatibility with Other Tools: Your crimping tool should work well with your wire strippers and cutters for consistent results.
You also want a crimping tool with a high-leverage design. This feature reduces hand fatigue and helps you make better crimps. Many professional electrician tools include a ratchet mechanism. This ensures every crimp is tight and consistent, which is important for thin cables where mistakes can cause failures. Ergonomic handles make long jobs easier on your hands.
Tip: Always test your crimped connections by giving them a gentle tug. A good crimp will not come loose.
A quality crimping tool belongs on every list of must have electrician tools. It helps you create safe, long-lasting electrical connections and keeps your work up to code.
Electrical Tape
Electrical tape is another must have electrician tool that you will use every day. This tape insulates wires and protects them from moisture, heat, and abrasion. You use electrical tape to cover exposed wires, secure loose connections, and bundle cables together. It is essential for preventing short circuits and accidental contact with live wires.
Choose UL-listed and CSA-certified electrical tapes for your electrician tools kit. These tapes meet strict safety standards and provide reliable insulation. Electrical tape resists heat and moisture, so you can use it indoors or outdoors. Strong adhesive keeps the tape in place, even in tough conditions.
Here are some of the most effective uses for electrical tape:
Insulating and protecting exposed wires
Securing loose wire connections
Bundling wires for better organization
Color-coding wires to reduce errors and make troubleshooting easier
Note: Color-coded electrical tape helps you identify wires quickly. This reduces mistakes and improves safety on the job.
You should always keep several rolls of electrical tape in your must have electrician tools. It is a simple tool, but it plays a big role in keeping your work safe and organized.
Cable Ties
Cable ties are essential for every electrician. You use them to bundle wires, secure cables, and keep your work neat. Good cable management prevents tripping hazards and makes future repairs easier. Cable ties come in many sizes and strengths, so you can match them to the job.
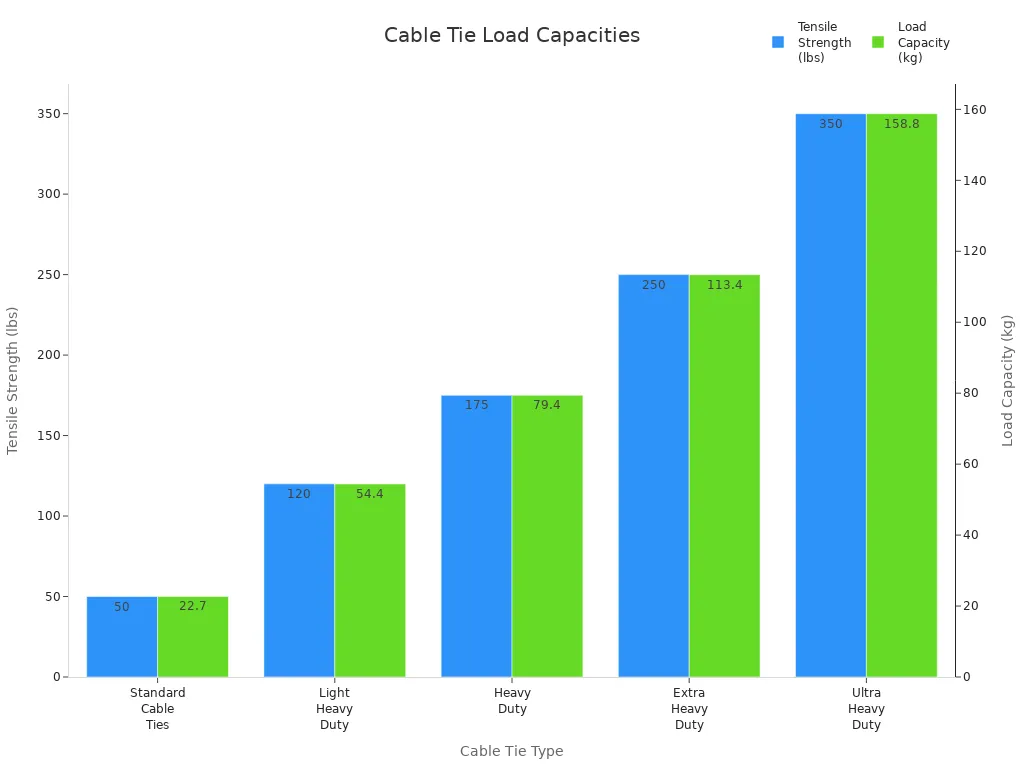
When you select cable ties for your electrician tools, consider the load capacity. Light-duty ties handle small bundles, while heavy-duty ties secure large or critical loads. For example, light-duty cable ties have a tensile strength of 18-50 lbs, while heavy-duty ties can handle over 250 lbs. Always add a safety margin of 20-30% above your expected load to ensure reliability.
| Cable Tie Type | Approximate Tensile Strength (lbs) | Approximate Load Capacity (kg) |
| Standard Cable Ties | 50 | 22.7 |
| Light Heavy Duty | 120 | 54.4 |
| Heavy Duty | 175 | 79.4 |
| Extra Heavy Duty | 250 | 113.4 |
| Ultra Heavy Duty | 350 | 158.8 |
Stainless steel cable ties offer even higher strength and resist extreme temperatures, making them ideal for harsh environments.
![Bar chart comparing tensile strength and load capacity for different cable tie types]()
You should also consider the material, size, and environmental conditions. Nylon ties work well for most indoor jobs, while stainless steel ties handle outdoor or high-temperature work. Always choose cable ties with a tensile strength higher than your expected load.
Tip: Cut off excess cable tie tails after installation. This keeps your work area safe and tidy.
Cable ties are must have electrician tools for anyone who wants to keep their wiring organized and secure. They help you maintain a professional appearance and improve safety on every project.
Measuring and testing tools
![Measuring and testing tools]()
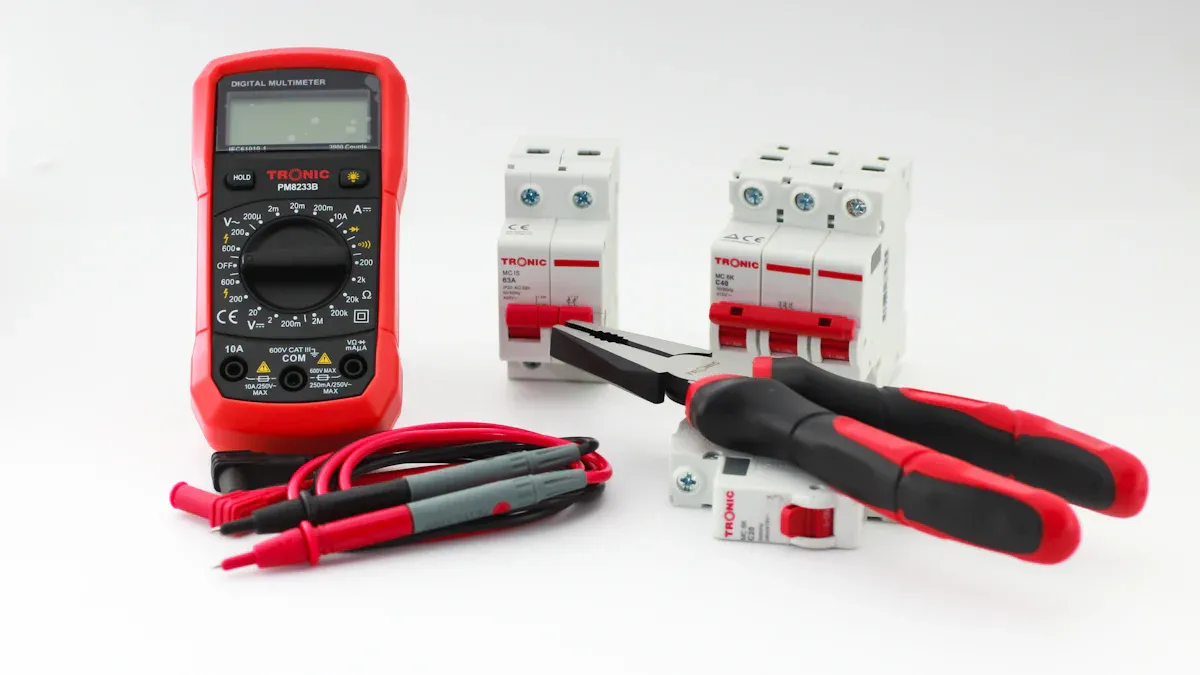
Multimeter
A multimeter is one of the most important tools for any electrician. You use it to measure voltage, current, resistance, and sometimes even frequency or capacitance. A digital multimeter gives you quick and accurate readings, which helps you troubleshoot electrical problems safely. Many electricians rely on a digital multimeter for both residential and industrial work.
Professional electrical work requires a multimeter that meets strict accuracy standards. Manufacturers specify accuracy values, such as 0.005% of reading plus 0.0035% of range, valid for one year. You should recalibrate your multimeter regularly to keep it reliable. Certified technicians in ISO/IEC 17025 accredited labs provide the best calibration. This ensures your measurements stay safe and accurate.
A digital multimeter often includes features like auto-ranging, data hold, and integrated non-contact voltage detection. These features make your job easier and safer. You can use a multimeter as a circuit tester to check for live wires, faulty connections, or broken circuits. Always choose a model with clear markings and a sturdy case.
Tip: Store your digital multimeter in a dry place and check the batteries often. A well-maintained tool gives you the best results.
Voltage Tester
A voltage tester helps you quickly check if a wire or outlet has voltage. You use this tool before starting any electrical work to make sure the circuit is safe. Most voltage testers have visual or audible indicators. Some models use lights, while others beep when they detect voltage.
Voltage testers come in two main types: contact and non-contact. Non-contact testers are very popular because you do not need to touch the wire. You just hold the tester near the wire, and it tells you if voltage is present. This saves time and reduces the risk of electric shock. However, non-contact testers can sometimes miss low voltages or give false readings. Always follow up with a more reliable circuit tester or multimeter for critical jobs.
Voltage testers are insulated to protect you from current transfer. Many models include automatic shutoff and battery life indicators for extra safety. You should always use the “live-dead-live” test. This means you test a known live circuit, then the circuit you want to check, and then a live circuit again. This process ensures your tester works correctly.
| Tool Type | Best Use Case | Example Feature |
| Non-contact Tester | Quick voltage checks, no direct contact | Pocket-sized, auto shutoff, LED alerts |
| Contact Tester | More reliable, direct measurement | Audible and visual indicators |
Approved Voltage Indicator
An approved voltage indicator is a step up in safety and reliability. You use this tool to confirm the presence or absence of voltage in a circuit. Approved voltage indicators meet strict safety standards, such as CAT ratings and transient protection. These tools are rated for the circuits they test and include features like fused electronics.
You should always choose an approved voltage indicator from a trusted manufacturer. These tools last longer and give more reliable results than generic testers. Many electricians use them for long-term safety, especially when working on high-voltage systems. Approved voltage indicators help you avoid accidents by providing clear, accurate readings.
Voltage indicators often include both visual and audible signals. Some models also have battery life indicators and automatic shutoff. Always follow safety standards like NFPA 70E and OSHA when using these tools. For full safety, use a direct-contact tester after a non-contact test. This double-checks that the circuit is truly safe.
Note: Multimeters and approved voltage indicators provide the most reliable and safe testing. They follow strict design standards and certifications.
A well-chosen set of measuring and testing tools helps every electrician work safely and efficiently. You should always keep a digital multimeter, voltage tester, and approved voltage indicator in your toolkit. These tools help you diagnose problems, confirm safe conditions, and meet professional standards.
Continuity Tester
A continuity tester is a simple but powerful tool that helps you check if an electrical circuit is complete. You use it to make sure current can flow from one point to another. This tool is important for every electrician because it helps you find problems before you turn on the power.
You often use a continuity tester to:
Check if wires are connected properly in outlets, switches, and other devices.
Find broken wires or poor connections that could cause trouble later.
Test fuses and switches to see if they work as they should.
Make sure protective earth and bonding conductors are continuous and safe.
Troubleshoot circuits by finding open or unintended connections.
When you use a continuity tester, you connect its probes to two points in the circuit. If the circuit is complete, the tester will beep or light up. This quick feedback lets you fix problems right away. You should always test continuity before energizing a circuit. This step keeps you safe and helps you follow wiring regulations.
Tip: Always turn off the power before using a continuity tester. This protects both you and your tools.
Tape Measure
A tape measure is a must-have for every electrician. You use it to measure distances when installing outlets, running conduit, or cutting cable. Choosing the right tape measure makes your work faster and more accurate.
Look for these features in a good tape measure:
| Feature | Why It Matters |
| Length (25 feet) | Covers most jobs, both big and small |
| Dual Markings | Shows both imperial and metric units for flexibility |
| Clear Numbers | Easy to read, reduces mistakes |
| Durable Build | Withstands drops and tough job sites |
| Non-slip Grip | Helps you hold the tape securely |
| Strong Lock | Keeps the tape in place while you mark or cut |
| Magnetic Tip | Sticks to metal surfaces, making solo work easier |
For most indoor jobs, a 25-foot tape measure works best. Some electricians use longer reel tapes for outdoor work, but these are less precise for small tasks. A tape measure with a smooth blade and reliable lock helps you measure quickly and accurately.
Note: Choose a tape measure with graphic markings for standard framing increments. This feature saves time during installation.
Level
A level helps you make sure your work is straight and even. You use it when mounting electrical boxes, outlets, or panels. A crooked installation not only looks bad but can also cause problems with covers and connections.
Most electricians prefer a small torpedo level. This type fits easily in your tool belt and works well in tight spaces. Some levels have magnets, so you can stick them to metal surfaces for hands-free use. Always check that your level is accurate before starting a job.
Using a level shows attention to detail. Straight lines and even installations make your work look professional and help everything fit together properly.
Tip: Keep your level clean and store it in your tool bag to prevent damage.
Electrician tools for installation
Electric Drill
You need an electric drill for almost every installation job. This tool helps you make holes in wood, metal, plastic, and even masonry. Most electricians prefer cordless drills because they offer flexibility and reduce the need for extension cords. Cordless models use rechargeable batteries, so you can work anywhere on the jobsite. Some tasks require more power, so you might choose a corded drill for heavy-duty work.
When you select an electric drill, look for these important features:
| Feature | Description | Why It Matters for Electricians |
| Power | Corded drills use wattage (500-1000W); cordless use voltage (9.6-32V) | More power means you can drill tougher materials |
| Speed | Variable speed, reverse function, slow start | Lets you control drilling for different jobs |
| Chuck Size & Type | 3/8 inch for light duty, 1/2 inch for heavy duty; keyless chucks for quick bit changes | Fits more drill bits and saves time |
| Hammer Action | Hammer mode for drilling into concrete or brick | Needed for masonry work |
| Torque Control | Adjustable clutch to prevent overdriving screws | Protects materials and fasteners |
| Handles | Pistol grip, auxiliary handle for stability | Reduces fatigue and improves control |
| Battery Types | Replaceable Ni-Mh or Ni-Cd batteries | Keeps your power tools ready for long jobs |
| Depth Stop | Prevents drilling too deep | Ensures consistent hole depth |
You should always match your drill to the task. For example, use a hammer drill for concrete or brick. For most electrical work, a drill driver or standard drill works well. Many modern power tools include LED lights and ergonomic grips to make your work easier and safer.
Tip: Keep your drill batteries charged and carry a spare. This helps you avoid downtime on the job.
Drill Bits
Drill bits are just as important as the drill itself. You need the right bit for the material you are working with. Using the wrong bit can damage your power tools or ruin the work surface. Electricians often use several types of drill bits during installation.
Here is a quick guide to common drill bit materials:
| Drill Bit Material | Advantages | Typical Use in Electrical Installation |
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | Affordable, easy to sharpen, long lifespan | Wood, plastic, soft metals |
| Cobalt (HSCO) | Durable, stays sharp, handles hard metals | Stainless steel, cast iron, titanium |
| Carbide | Extremely hard, heat resistant | Steel boxes, panels, tough materials |
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | Reduces friction, extends bit life | Steel, metal junction boxes |
You should always choose the right bit for the job. For example, use carbide bits for drilling through steel panels. HSS bits work well for wood and plastic. Many electricians recommend brands like Greenlee for steel and Milwaukee for wood.
Note: Replace dull bits quickly. Sharp bits make cleaner holes and protect your power tools.
Fish Tape
Fish tape is a specialized tool that helps you pull wires through conduit, walls, or ceilings. You feed the fish tape through the pathway, attach the wire, and pull it back. This tool saves you time and effort, especially in long or complex runs.
Most electricians use steel or fiberglass fish tapes. Steel tapes are strong and work well for straight runs. Fiberglass tapes bend easily and help you navigate tight spaces or bends. You should choose the length and material based on your typical jobs.
Fish tape makes wire pulling faster and easier.
It reduces the risk of damaging wires during installation.
You can use it in both residential and commercial settings.
Tip: Clean and inspect your fish tape after each use. This keeps it working smoothly and extends its life.
Modern power tools and specialized equipment like fish tape, conduit benders, and modular storage solutions help you work more efficiently. These tools are essential for every electrician who wants to complete installations safely and quickly.
Conduit Bender
You need a conduit bender to shape electrical conduit for clean and safe wiring runs. This tool helps you bend metal or PVC conduit at precise angles. You use it to route wires around corners, obstacles, or along walls. Every electrician should know how to use a conduit bender because it keeps installations neat and up to code.
A conduit bender usually has markings for common angles like 30°, 45°, and 90°. These markings help you make accurate bends without guessing. You place the conduit in the bender, step on the foot pedal, and pull the handle to create the bend. The process feels simple, but it takes practice to get perfect results every time.
There are two main types of conduit benders:
Hand benders: Best for small-diameter conduit (up to 1 inch). You use these for most residential and light commercial jobs.
Mechanical or hydraulic benders: Handle larger conduit sizes. These save time and reduce effort on big projects.
Tip: Always measure and mark your conduit before bending. This ensures you get the right length and angle for your installation.
You should check the manufacturer's instructions for your conduit bender. Each model may have unique features or markings. Some benders include a built-in level to help you keep bends straight. Others have reference charts for quick setup.
A good conduit bender helps you avoid kinks or flattened spots in the conduit. Smooth bends protect wires from damage and make pulling cables easier. You will find that using the right tool improves your work quality and saves time. Many electricians consider the conduit bender just as important as their power tools.
Hammer
A hammer is a basic but essential tool for every electrician. You use it to drive nails, secure electrical boxes, and fasten straps or clamps. A hammer also helps you remove old hardware or tap conduit into place. While it may seem simple, choosing the right hammer makes your job easier and safer.
Electricians often prefer a lightweight hammer with a smooth face. This design prevents damage to surfaces and reduces fatigue during long jobs. A straight claw helps you pull nails or pry open boxes. Some hammers have fiberglass or insulated handles for extra safety.
Here are some ways you use a hammer in electrical work:
Mounting electrical boxes to studs or walls
Fastening cable staples or straps
Removing old fasteners or hardware
Adjusting conduit or fittings
Note: Always wear safety glasses when using a hammer. Flying debris can cause serious injuries.
You should keep your hammer in good condition. Check the handle for cracks and make sure the head stays tight. A well-maintained hammer lasts for years and helps you work efficiently. While power tools handle many tasks, a hammer remains a must-have for quick fixes and precise adjustments.
A complete electrician toolkit includes both advanced power tools and reliable hand tools like the conduit bender and hammer. These tools help you install wiring safely and keep your work looking professional.
Safety and organization
![Safety and organization]()
Insulated Gloves
Insulated gloves protect you from electric shock when you work with live wires or electrical panels. Every electrician should use gloves that meet strict safety standards. In the United States, gloves must comply with ASTM D120. Internationally, IEC 60903 and EN 60903 set the rules. These standards make sure the gloves can handle the voltage you face on the job.
You need to pick gloves based on the voltage level. Gloves come in classes, such as 00 and 0 for low voltage, and classes 1 through 4 for higher voltages. Always check the label before you use a new pair. Before each use, inspect your gloves for holes, cracks, or signs of wear. Inflate them with air to spot hidden damage. Store your gloves in a cool, dry place, away from sunlight and chemicals. Many experts recommend wearing leather protectors over your insulated gloves. This extra layer guards against cuts and punctures.
Tip: Replace gloves that show any damage. Damaged gloves cannot protect you from electric shock.
Safety Glasses
Safety glasses keep your eyes safe from flying debris, sparks, and dust. You need them for every electrical job, even if you think the risk is low. Occupational safety guidelines list safety glasses as essential personal protective equipment (PPE) for electricians. Choose glasses that fit well and do not slip. Some models wrap around your face for extra protection.
You can find safety glasses with anti-fog coatings and scratch-resistant lenses. These features help you see clearly and keep your glasses in good shape. For jobs with higher risks, use goggles or a face shield. Always clean your glasses after each use and store them in a case to prevent scratches.
Note: Never start electrical work without eye protection. Even a small accident can cause serious injury.
Tool Belt or Tool Bag
A tool belt or tool bag helps you stay organized and work faster. You can keep your most-used tools within reach, which saves time and reduces trips back and forth. Many tool belts have special pockets for screwdrivers, pliers, and tape. Some even have rings for electrical tape and clips for your tape measure.
Look for these features in a good tool belt or bag:
Multiple compartments for different tools
Secure pockets to prevent tools from falling out
Adjustable straps or suspenders for comfort and even weight distribution
Molded bases to keep the bag upright and protect tools from wet surfaces
Small zippered bags for screws and wire nuts
Some electricians prefer backpacks or rolling cases. These options spread the weight across your back or let you pull heavy tools with ease. Modular tool boxes with stackable bins and drawers help you customize your storage. Good organization keeps your workspace safe and helps you find the right tool quickly.
| Feature | Benefit |
| Specialized pockets | Quick access to specific tools |
| Secured retention | Prevents accidental drops |
| Even load distribution | Reduces strain and supports your health |
| Molded base | Protects tools from wet or dirty floors |
Tip: Organize your tool belt or bag at the start of each day. This habit helps you work more efficiently and safely.
Flashlight
A flashlight is a tool every electrician should carry. You often work in dark spaces, such as attics, basements, or inside electrical panels. Good lighting helps you see wires, connections, and hazards clearly. A reliable flashlight keeps you safe and helps you do your job well.
You should choose a flashlight that is bright and durable. Many electricians prefer LED flashlights because they last longer and use less battery power. Some models have adjustable beams, so you can focus on a small area or light up a whole room. A flashlight with a magnetic base or a hook lets you work hands-free. This feature is helpful when you need both hands for wiring or repairs.
Here are some features to look for in a good flashlight:
High brightness (measured in lumens)
Long battery life
Water and impact resistance
Compact size for easy carrying
Hands-free options (magnet, hook, or headlamp style)
Tip: Always keep spare batteries in your tool bag. A dead flashlight can slow you down and make your work unsafe.
Some electricians use headlamps instead of handheld flashlights. A headlamp gives you light wherever you look and keeps your hands free. This option works well in crawl spaces or when you need to climb ladders.
A quality flashlight helps you spot problems before they become serious. You can check for loose wires, damaged insulation, or signs of overheating. Good lighting also helps you avoid mistakes and work more efficiently.
Lockout/Tagout Kit
A lockout/tagout kit is a safety tool that protects you from accidental electrical shocks. When you work on electrical systems, you must make sure no one can turn the power back on by mistake. The lockout/tagout kit helps you do this.
You use the kit to lock switches, circuit breakers, or disconnects in the "off" position. You also attach a tag that warns others not to turn the power back on. This process keeps you and your coworkers safe while you work on wiring or equipment.
A basic lockout/tagout kit usually includes:
Padlocks with unique keys
Lockout hasps (for locking multiple switches)
Warning tags with space for your name and date
Circuit breaker lockouts
Plug lockouts
| Kit Item | Purpose |
| Padlocks | Secure switches or breakers in "off" mode |
| Hasps | Allow multiple locks on one device |
| Tags | Warn others about ongoing work |
| Breaker/plug lockouts | Fit specific devices for extra safety |
Note: OSHA requires electricians to use lockout/tagout procedures when working on electrical equipment. Following these rules can prevent serious injuries or even save lives.
You should always follow your company’s safety policies and local regulations. Before starting any electrical work, use your lockout/tagout kit to secure the power source. Double-check that the equipment cannot be turned on until you finish the job.
A lockout/tagout kit is a must-have for every electrician. It shows that you take safety seriously and helps you protect yourself and others on the job.
Quick reference checklist
Building your electrician toolkit does not have to feel overwhelming. Use this quick reference checklist to make sure you have every essential tool for safe and efficient electrical work. You can print this list or save it on your phone for easy access when shopping or organizing your gear.
️ Essential Electrician Tools Checklist
Tip: Choose tools from reputable brands like Newstar Hardware. Quality tools last longer and help you work more safely.
Electrician Tools at a Glance
| Tool Category | Example Tools | Why You Need Them |
| Cutting & Stripping | Wire cutters, strippers | Clean, safe wire prep |
| Gripping & Bending | Pliers, conduit bender | Secure, shape, and route wires |
| Fastening | Screwdrivers, nut drivers | Tighten or loosen connections |
| Measuring & Testing | Multimeter, voltage tester | Check circuits and ensure accuracy |
| Installation | Drill, fish tape, hammer | Make holes, pull wires, mount gear |
| Safety & Organization | Gloves, glasses, tool bag | Protect yourself and stay organized |
You should check your toolkit against this list before starting any project. Missing even one tool can slow you down or create safety risks. If you notice worn or damaged tools, replace them right away. Reliable tools help you finish jobs faster and with fewer mistakes.
You can trust brands like Newstar Hardware for durable, professional-grade tools. Investing in quality equipment pays off over time. You will notice better results and feel more confident on every job.
Keep this checklist handy. Review it often to keep your toolkit complete and ready for any electrical task.
A complete set of electrician tools keeps you safe and helps you do quality work. Review your toolkit often and fill any gaps you find. When you invest in high-quality tools, you gain many long-term benefits:
Tools last longer and perform better, saving you money.
Ergonomic and smart designs boost your efficiency.
Built-in safety features lower your risk of injury.
Good tools help you work faster and meet safety rules.
Share your favorite electrician tools or tips in the comments below!
FAQ
What are the most important electrical hand tools for beginners?
You should start with lineman’s pliers, wire strippers, insulated screwdrivers, a voltage tester, and a tape measure. These tools help you handle most basic electrical tasks safely and efficiently.
How do you know if a tool is safe for electrical work?
Look for insulation ratings and safety certifications like IEC 60900 or ASTM F1505. You should check for clear voltage markings and buy from trusted brands. Always inspect tools for damage before use.
Can you use regular pliers or screwdrivers for electrical work?
No, you should use only insulated tools designed for electrical work. Regular tools do not protect you from electric shock. Insulated handles and safety certifications keep you safer.
How often should you replace or inspect your electrician tools?
Inspect your tools before every use. Replace any tool that shows signs of wear, cracks, or damage. Regular checks help you avoid accidents and keep your work reliable.
What is the difference between a voltage tester and a multimeter?
A voltage tester checks if voltage is present. A multimeter measures voltage, current, and resistance. You use a voltage tester for quick safety checks. You use a multimeter for detailed troubleshooting.
Why is a lockout/tagout kit important for electricians?
A lockout/tagout kit prevents accidental power restoration while you work. You use it to lock switches or breakers and attach warning tags. This keeps you and others safe from electric shock.
How do you organize your electrician tools for maximum efficiency?
Use a tool belt, bag, or modular box with labeled compartments. Keep your most-used tools within easy reach. Organize small items like screws and wire nuts in zippered pouches or small containers.
What should you do if you accidentally cut a live wire?
Stop working immediately. Move away from the area. Turn off the power at the main breaker. Check yourself for injuries. If you feel a shock or burn, seek medical help right away.